Automated and Interpretable Detection of Hippocampal Sclerosis - a MELD study
Hippocampal Sclerosis (HS) is a form of atrophy affecting the hippocampus that can cause epileptic seizures. When identified and surgically removed, patients can be cured from epilepsy seizures. Accurate detection of HS on MRI scans and determining which side of the brain is affected is therefore essential for planning a successfull surgery.
In work published in published in Annals of Neurology in 2024, the Multi-centre Epilepsy Lesion Detection (MELD) Project introduced AID-HS, an automated tool that can detect HS and determines the affected hemisphere (lateralise) and generates interpretable patients reports summarising the results.
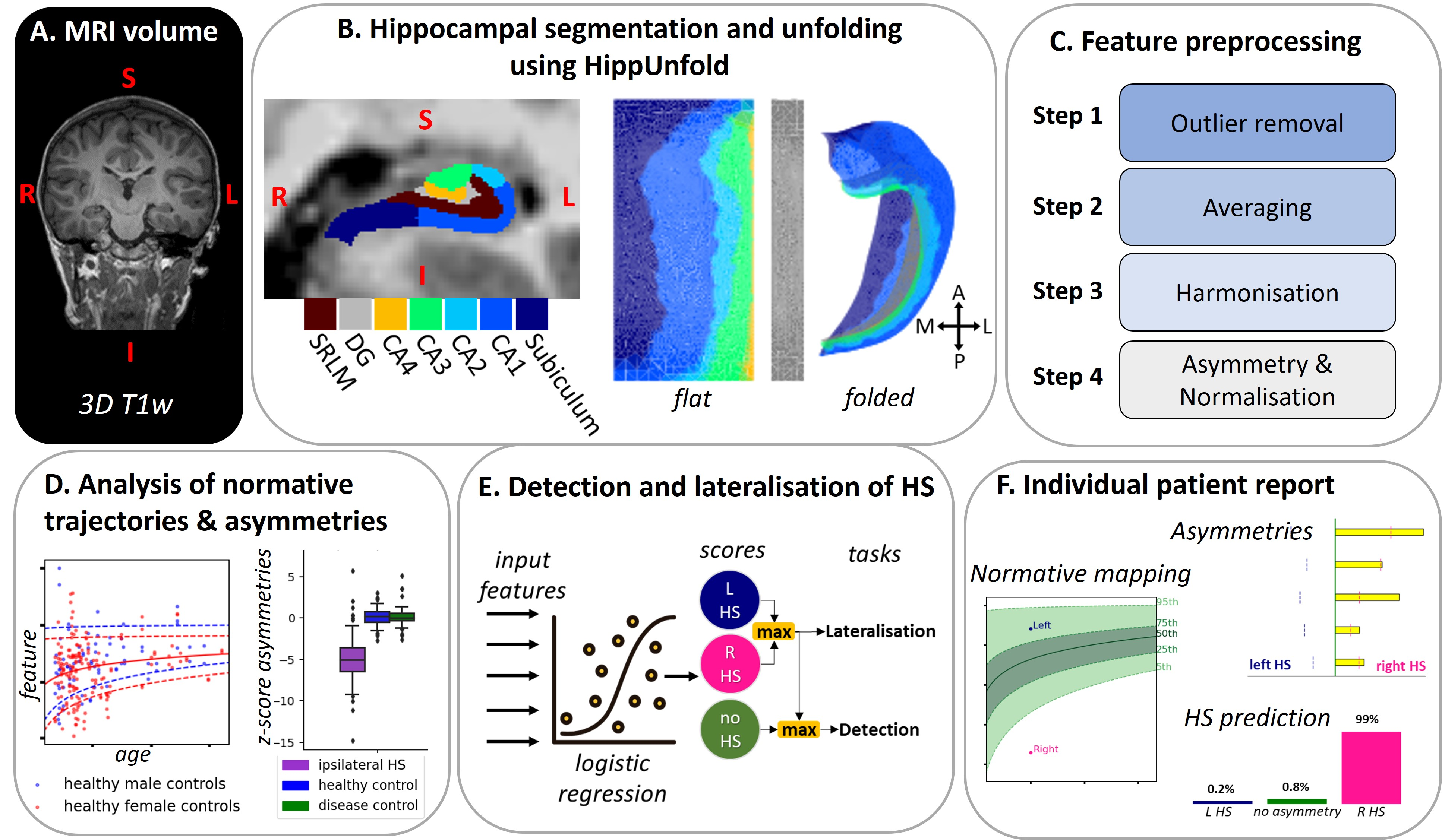
AID-HS extracts hippocampal volume and surface-based features (such as thickness, curvature, and gyrification of the hippocampus) using the software HippUnfold. These features are then normalised by the features of a large cohort of healthy controls, and asymmetries between the left and right hippocampi are calculated. The resulting asymmetry features were used to train a logistic regression model at detecting and lateralising HS. AID-HS also produces interpretable reports that show each patient’s hippocampal features relative to normative “growth charts” of the healthy population, visualise asymmetries, and present the model’s predictions.
Results
The tool was developed using MRI data from 154 patients with HS, 90 patients with focal cortical dysplasia (another epilepsy-associated lesion), and 121 healthy controls from four hospitals worldwide. AID-HS detected HS with 90.1% sensitivity and 94.3% specificity and correctly lateralised HS in 97.4% of patients. Similar performance was observed when the tool was tested on an independent multicentre cohort of 275 patients and 161 controls, demonstrating its ability to adapt to new data different from the one used to train the model.
Running the pipeline on new patients
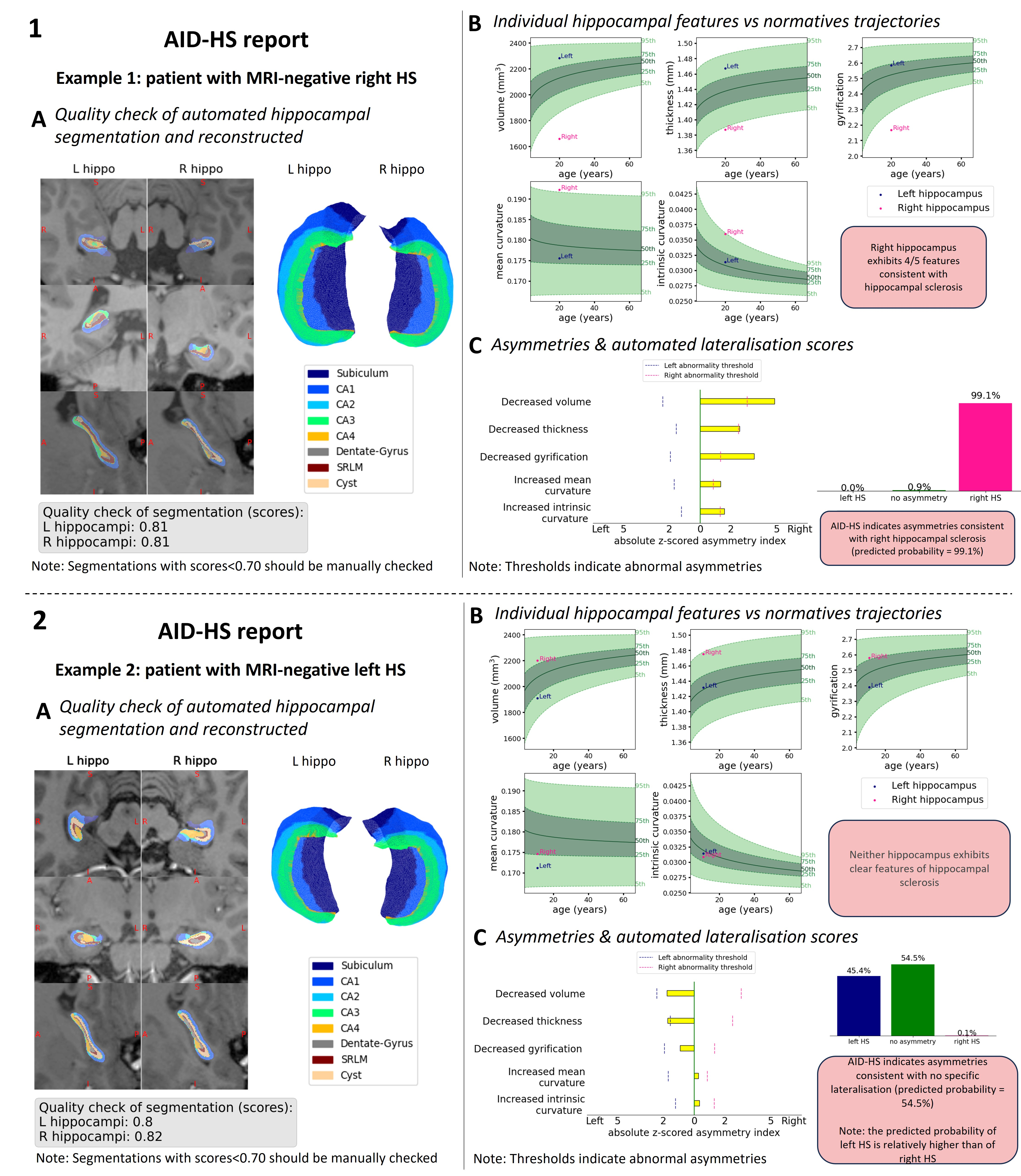
The pipeline generates an individualised patient report that includes:
- A visualisation of the hippocampal segmentation and the pial surfaces reconstructed with HippUnfold, with dice scores assessing how well the segmentation matches the HippUnfold atlas
- Each hippocampal feature plotted against normative trajectories of healthy population
- The magnitude and direction of asymmetry features relative to abnormality thresholds
- Automated lateralisation scores from the AID-HS classifier, showing the probability of left HS (blue), right HS (pink), or no significant asymmetry (green)
AID-HS worldwide use
AID-HS is open-source and available on macOS, Windows, and Linux via Github. Tutorial videos to help install and uses the tool are available on our Youtube channel
Written with the assistance of ChatGPT